Xhyper剖析[4]--XhyperCPU虚拟化
5.1 vcpu构建
在 CPU 虚拟化中,首先明确一个概念就是 Guest VM 依然还是运行在实际的物理 CPU 上,那么这里提到的 VCPU 是一个什么概念呢?
- VCPU 的运行与进程的上下文切换是类似的,当 Guest VM 需要切换到 VCPU 运行时,Hypervisor 就将 VCPU 对应的 Guest VM 的上下文恢复到对应的物理 CPU 中。当 Guest OS 由于执行一些敏感指令、访问没有权限的内存等情况时,会陷入运行在更高特权级的 Hypervisor,然后 Hypervisor 负责将物理 CPU 的状态保存到 VCPU 上下文中。所以我们这里就可以理解 VCPU 就是对物理 CPU 资源的抽象,Hypervisor 实现了物理 CPU 对 Guest VM 的时间复用。
- 在 Hypervisor 中可以控制所有的系统资源,包括之前讲到的物理内存、IO 设备、中断、指令等。Hypervisor 可以配置 Guest VM 在执行到敏感指令时触发异常,该异常会被路由到 EL2 的 Hypervisor 中,然后可以对这些敏感指令进行模拟。
首先对Guest VM进行抽象:
- 一个VM包括其需要的CPU个数,二阶段地址转换的页表基地址寄存器和VCPU集合
// vm.h |
vcpu需要保存的内容如下:
enum vcpu_state { |
- 保存通用寄存器
regs和系统寄存器sys_regs
在Xhyper中一个物理cpu对应一个vcpu
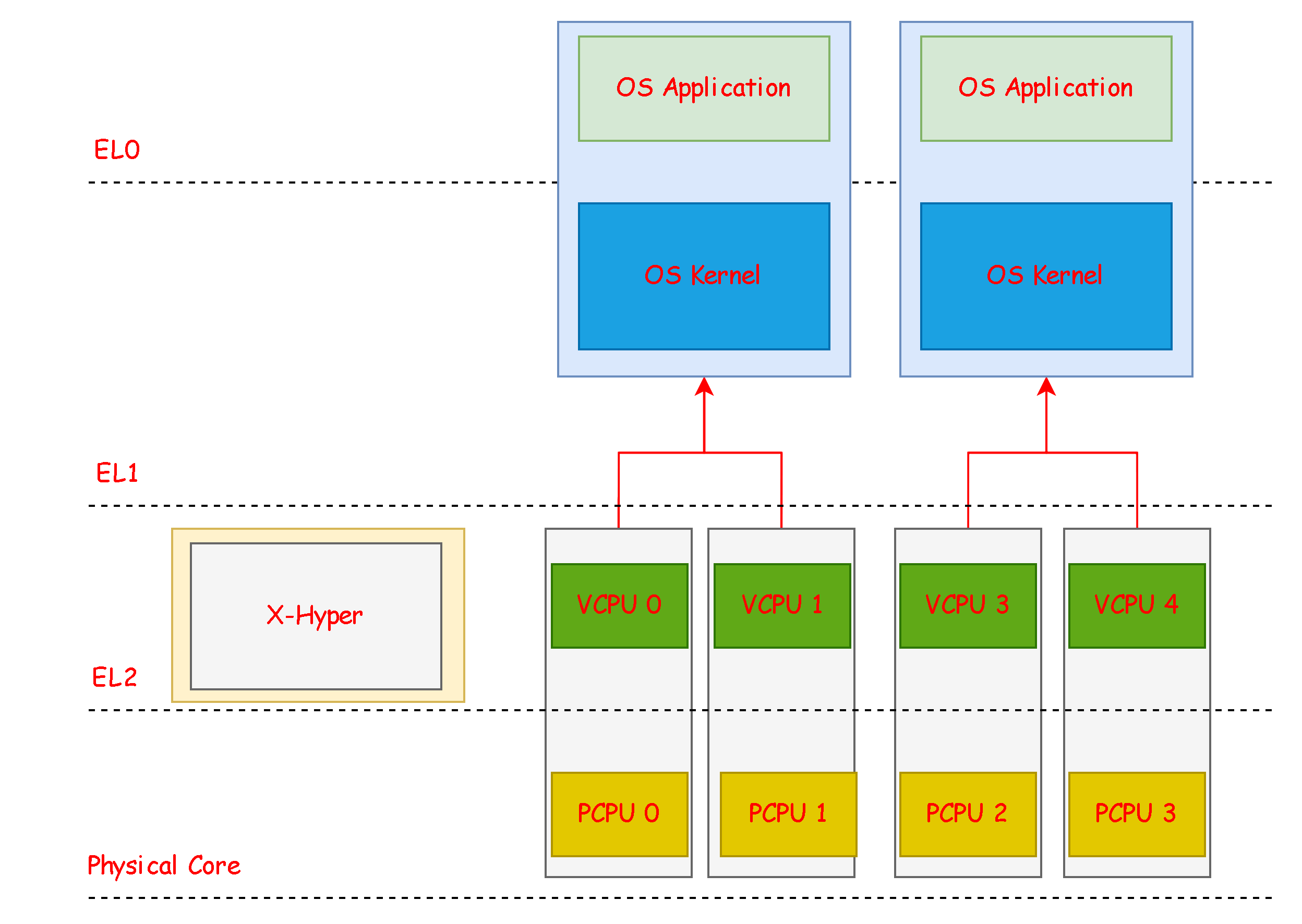
创建一个vcpu
vcpu_t *create_vcpu(vm_t *vm, int vcpuid, u64 entry) |
- 修改regs.spsr,该值在进入 Guest VM 之前会被加载到 SPSR_EL2 寄存器中,可以保证异常返回到 Aarch64 状态的 EL1。
- 修改regs.elr,该值在进入 Guest VM 之前会被加载到 ELR_EL2 寄存器中,可以保证异常返回到 Guest VM 的入口地址。
- 修改sys_regs.mpidr_el1,该值在进入 Guest VM 之前会被加载到 MPIDR_EL1 寄存器中,能够使 Guest VM 看到虚假的核号。
- 修改sys_regs.midr_el1,该值在进入 Guest VM 之前会被加载到 MIDR_EL1 寄存器中,能够使 Guest VM 看到虚假的 CPU 身份信息
选择cpu
static void switch_vcpu(vcpu_t *vcpu) |
- 首先将当前 vpu 的地址保存到 TPIDR_EL2 寄存器中,这样做的目的是当 Guest VM 的该 VCPU 发生异常时,Hypervisor 可以通过读取 TPIDR_EL2 来获取发生异常的 VCPU。
- 修改 VTTBR_EL2,保证该 Guest VM 可以访问其 IPA。
- 然后将 VCPU 中的通用寄存器和系统寄存器的值加载到实际的物理寄存器中。
- 调用 switch_out 返回 Guest VM。
有个重要的函数switch_out:
- 从
tpidr_el2取出vcpu的地址,根据此指针去恢复寄存器的值 - 恢复完成寄存器的值后,调用
eret指令返回EL1执行
# vector.s |
5.2 启动cpu 0
在Xhyper的main.c的hyper_init_primary函数中首先调用了hyper_setup();
/* Provides configuration controls for virtualization */ |
vbar_el2寄存器是异常向量表地址寄存器,代表产生异常时陷入EL2时的异常向量表的地址,这里设置成了hyper_vector
hyper_vector定义在vector.s中,关于arm异常向量表的知识参考2.3节
.macro save_vm_regs |
- 可以看见当异常为
vector_el1_sync时会首先调用save_vm_regs保存当前cpu的执行状态到对应的vcpu中 - 然后调用
el1_sync_proc处理异常
//el1_sync.c |
esr_el2寄存器的ec字段保存了异常产生的原因,即根据ec字段的值来判断是什么异常- 0x16:表示客户机执行的 HVC 指令触发了异常,且被陷阱到 EL2。
- 0x17: Trapped SMC 指令(由 HCR_TSC 触发)。
esr_el2寄存器的iss字段提供更详细的异常信息
通过switch_out函数就会返回到EL1中执行,入口函数为guest os的_start函数:
.section .text, "ax" |
- 此函数会比对当前的
core id如果为0,则会跳转到vm_primary_init函数执行,如果core id为1则会跳转到vm_secondary_init函数执行
vm_primary_init函数如下:
int vm_primary_init() |
smc_call函数可以用来启用另外一个cpu核心主要是调用smc指令来实现
.global smc_call |
smc指定对应的id如下:
/* https://developer.aliyun.com/article/1205031 */ |
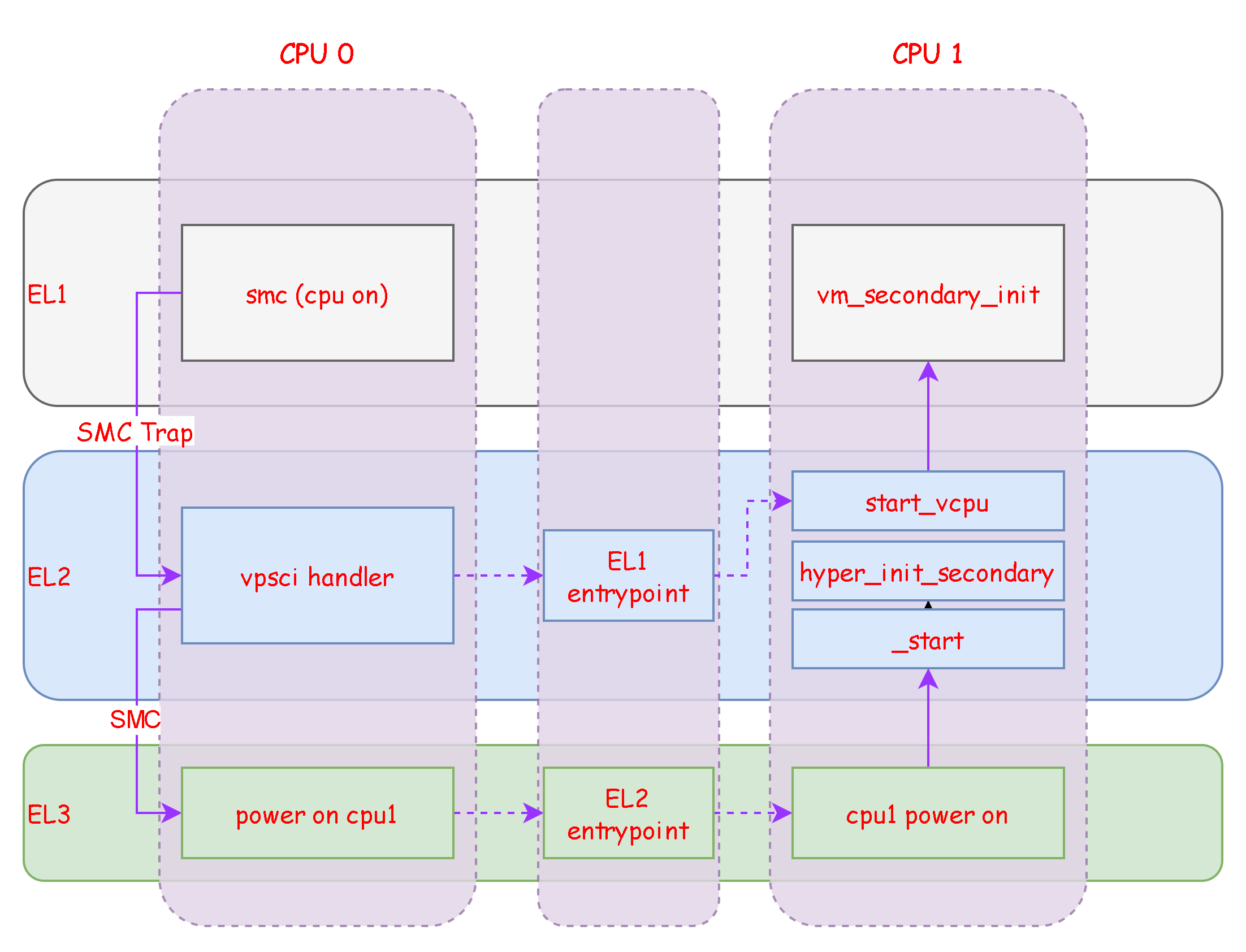
5.3 启动cpu 1
通过smc指令就会从guest os陷入到el2然后通过查找异常向量表调用到el1_sync_proc()函数,根据esr_el2的ec字段的值来判断进行下一步调用
如果是0x17即smc call的话会进入到hvc_smc_handler处理
//el1_sync.c |
vpsci_trap_smc进一步处理:
// vpsci.c |
当调用的id号为PSCI_SYSTEM_CPUON时会去唤醒一个cpu核心:
- 这里有个重要点,将唤醒的cpu对应的vcpu的返回地址设置为了
entry_addr,这样被唤醒的cpu从el2返回到el1执行时就会返回到entry_addr处执行
static s32 vpsci_cpu_on(vcpu_t *vcpu, u64 funid, u64 target_cpu, u64 entry_addr) |
唤醒的cpu核心在el2的执行地址为_start:
.section .text, "ax" |
start函数会比对当前的core id是0还是1,如果是1,则说明是被唤醒的一个新的core,因此会跳转到hyper_init_secondary函数执行
int hyper_init_secondary() |
到这里core 1也已经被启动了,core 1通过start_vcpu函数就可以返回到el1执行,core 0在处理完成el1来的异常后也会返回到el1
vector_el1_sync: |
整体的流程如下:
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 TimerのBlog!



![ARM64-Trust-Firmware[3]-BL1解析](/2026/01/24/ARM64-Trust-Firmware-3-BL1%E8%A7%A3%E6%9E%90/17692290470595.png)
![ARM64-Trust-Firmware[2]-启动ATF](/2026/01/24/ARM64-Trust-Firmware-2-%E5%90%AF%E5%8A%A8ATF/17692287555201.png)
![ARM64-Trust-Firmware[1]-ARM安全架构](/2026/01/24/ARM64-Trust-Firmware-1-ARM%E5%AE%89%E5%85%A8%E6%9E%B6%E6%9E%84/17692284856153.png)