开启调试功能
1. bug修改
之前的代码中留下了一个bug,在app.c中,通过sys_gettime的系统调用来获取时间,这里是有问题的,从内核返回的值不知道为啥不对,问题出在syscall函数上,以前的写法是:
size_t syscall(size_t id, uintptr_t arg1, uintptr_t arg2, uintptr_t arg3) { |
不知道为啥这样写就有问题,好像这个ret定义了就会导致返回的值不对,从内核返回的值是放在a0寄存器中,把上面的代码替换了一下:
uint64_t syscall(size_t id, reg_t arg1, reg_t arg2, reg_t arg3) { |
这样内核的返回值就没问题了,来测试一下sys_gettime()系统调用,在task3中调用:
void task3() |

时间打印成功,由于定时中断的分频系数被修改成了500,所以这里是以2us为单位返回时间。
2.开启调试功能
之前在调试内核的时候,我一直没使用gdb去调试程序,因为代码不算困难,我用printf去打印调试也花费不了太多时间,最近在倒腾mmu,我觉得有必要用gdb去调试了,再vscode中调试是非常方便的,当然也可以直接在终端中调试。
2.1 终端使用GDB调试
在os的makefile中添加调试选项:
- 编译时需要生成调试信息,添加
-g的编译选项
CFLAGS = -nostdlib -fno-builtin -mcmodel=medany -g |
- 指定调试器,这里的调试器需要使用riscv编译工具链中提供的
riscv64-unknown-elf-gdb,当然还有一个gdb-multiarch也是可以的,但是联合vscode时不知道为啥不能检测寄存器的值
GDB = riscv64-unknown-elf-gdb |
- 配置调试选项,新建一个
gdbinit文件,gdb调试qemu程序时,需要将端口映射到1234
set disassemble-next-line on |
- 修改
run.sh,添加如下选项就可启动调试了,此时qemu会作为gdb的服务端,端口号为1234
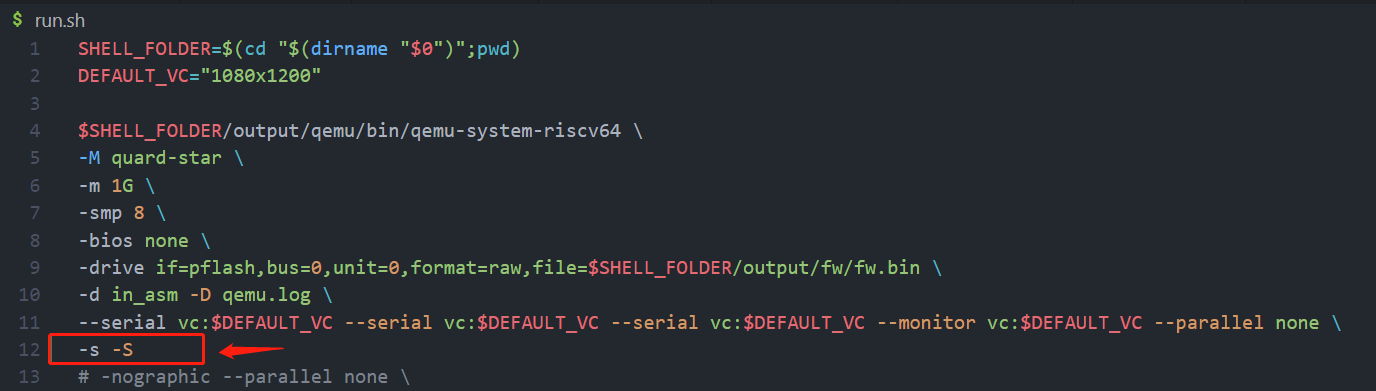
- 开启调试,这样make clean时不会删除
os.elf文件,在启动qemu后就可通过make debug来开启调试了
.PHONY : debug |
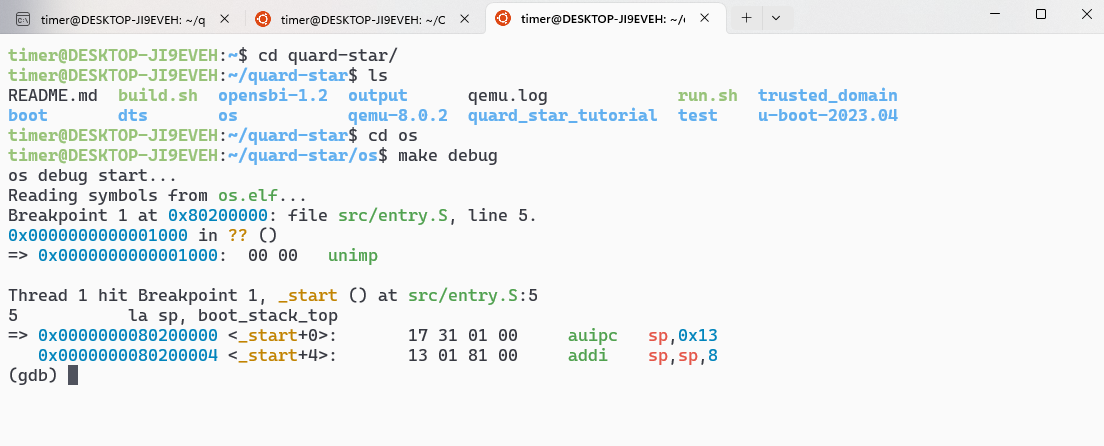
这样就可以在终端中调试了。
2.2 GDB+Vscode调试
新建.vscode文件夹,在此文件夹中新建两个文件
launch.json,需要将调试器指定为riscv64-unknown-elf-gdb,需要指定为你自己电脑上的编译工具链的gdb的位置,然后调试的program指定为:os.elf
{ |
task.json就是用来运行build.sh
{ |
launch.json设置官方文档:Configure launch.json for C/C++ debugging in Visual Studio Code
tasks.json设置官方文档:Tasks in Visual Studio Code
launch.json文件是VSCode启动程序的配置文件,task.json就是用于定义前置任务。若在launch.json中指定了preLaunchTask参数,则会去执行task.json中指定的命令。
${workspaceFolder}:项目文件夹在 VS Code 中打开的路径${file}:当前开打开(激活)的文件${relativeFile}:相对于{workspaceFolder}的文件路径${fileBasename}:当前打开文件的名称${fileBasenameNoExtension}:当前打开文件的名称,不带扩展名的${fileExtname}:当前打开文件的扩展名${fileDirname}:当前打开文件的文件夹名称
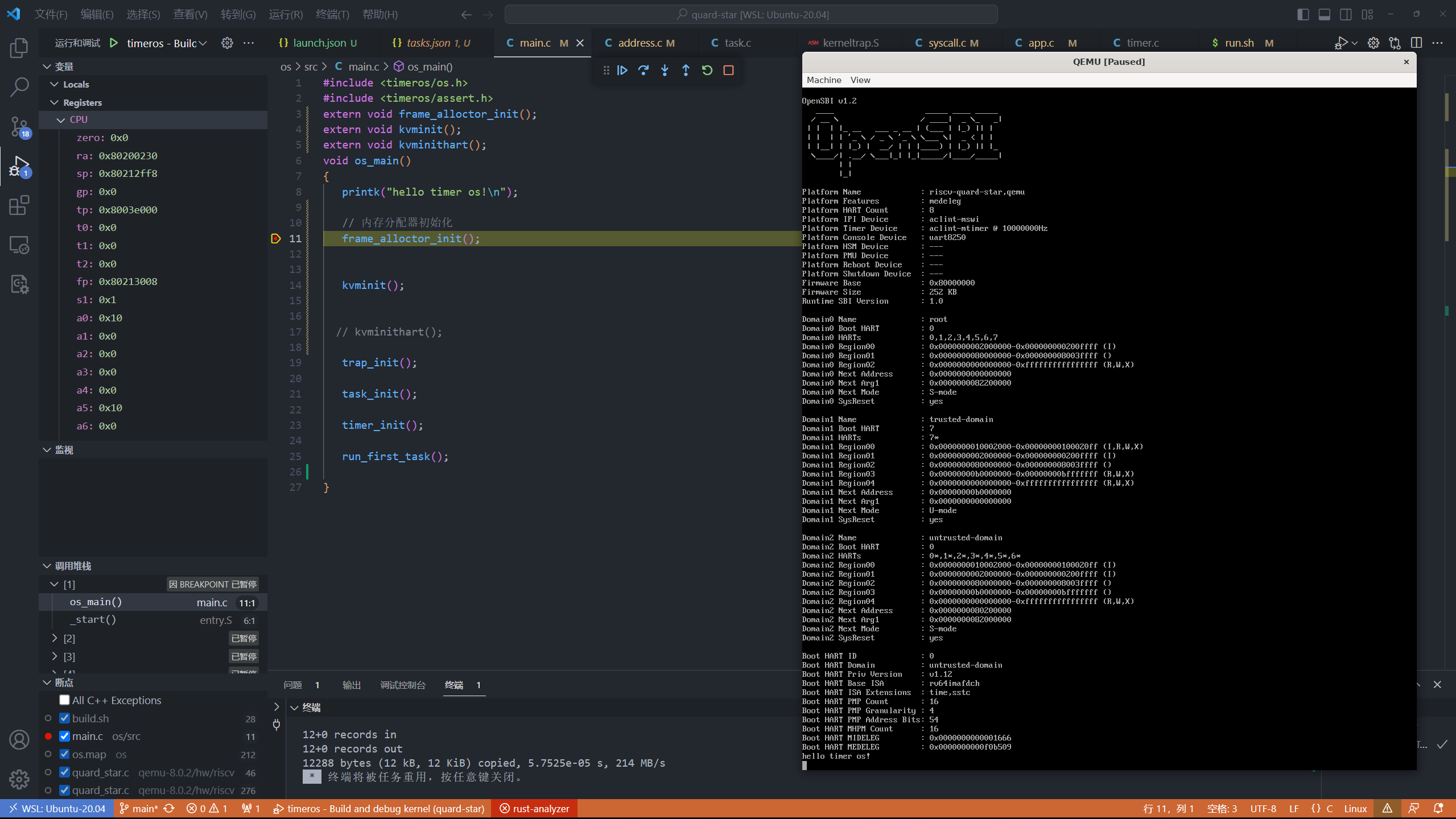
这样就可以在vscode中调试内核了
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 TimerのBlog!